Guide To Car Headlight Bulbs: Halogen, Xenon and LED

Published 6 November 2016
Most modern cars use one of 3 different types of car headlight bulbs:
- halogen – generally found on smaller more affordable cars.
- xenon – more likely on cars with sportier styling designed to have narrower headlight units.
- LED – tend to be reserved for luxury and sporting models as they are the most expensive to produce.
Halogen Bulbs
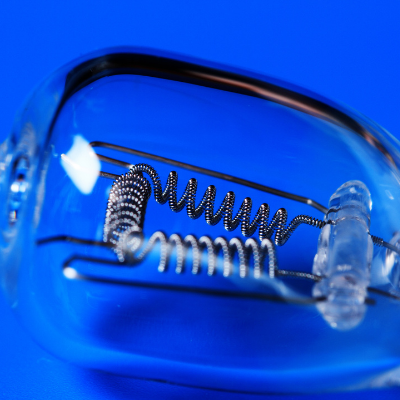
Halogen bulbs (sometimes called filament bulbs) are typically the standard bulbs in most cars.
Halogen bulbs use a tungsten filament and a mix of inert gases, usually nitrogen and argon, to create light.
They are widely used because they are cheap to produce and to replace.
While they’re popular, they’re not as bright or inefficient as other options.
The addition of a blue coating to the bulb will turn the colour of the light to be more white. The downside to this is a small reduction in light intensity.
Bulbs with a higher wattage produce more light but have a shorter lifespan.
The H4 is a double-filament headlight bulb that’s typically used in small cars.
The H17 and H18 bulbs are smaller, more powerful halogen bulbs, while the H8, H9 and H11 are self-sealing bulbs that don’t have to sit inside a watertight unit, so they’re often used as foglights.
Typical life expectancy: 2000 hours
Xenon or High-Intensity Discharge (HID) Bulbs

Xenon headlights are a popular choice for luxury cars, using metals and heat gases to create a bright blue or white glow.
You’ll be able to spot these headlights easily on the road, thanks to their ice white/blue tint and extreme brightness.
While the brightness and range of the light is impressive, xenon bulbs can dazzle other drivers and create glare.
Xenon HID (High Intensity Discharge) bulbs are filled with Xenon gas and contain two electrodes – one on each end of the tube-like bulb. When the bulb is switched on, an electric current passes between the two electrodes and the Xenon gas lights up. The Xenon gas is actually only used during the start-up of the bulb. Once the desired temperature inside the lamp is reached, other gases inside the bulb ensure it stays lit.
Although xenons generally last much longer than halogen bulbs, their light output can decrease over time, so eventually they won’t emit enough light to be safe for night use. Some manufacturers therefore recommend replacing xenon bulbs every three years.
You can convert your regular halogen bulb to xenon with a special kit, but these are not road legal in the UK.
Typical life expectancy: 10,000 hours
LED Car Headlights

LED or light emitting diodes are now replacing xenons on new cars, because they are more energy efficient, last longer and allow car makers to create signature light shapes.
Electricity is passed through one or more light-emitting diodes .
The light produced is similar in brightness to that of a xenon bulb, and produce very little heat so they’re more efficient and therefore cheaper to run.
LED bulbs are great for producing a light that is close to that of daylight and they offer less glare than other bulbs which means that they do not dazzle oncoming drivers.
LED bulbs can be more expensive than other car bulb types, but that’s off-set with the thousands of hours of trouble-free operation you can expect.
Typical life expectancy: 30,000 hours
Compass Vehicle Services Ltd offer:
nationwide car leasing – bad credit car finance – used car deals – personal leasing – business car leasing – best car lease deals – non-status car leasing
Back to all help and advice articles


